Outline
Understanding Business Risk in the Context of Large Companies
Understanding Business Risk
Introduction to Business Risk
Distinguishing Business Risk and Financial Risk
Comprehensive Analysis of Business Risks for Large Enterprises
Types of Business Risk Affecting Large Companies
Economic Risk: This encompasses the uncertainty derived from economic fluctuations. For large companies, economic risks can manifest in various forms — from exchange rate volatility affecting international transactions to shifts in consumer demand impacting sales. Economic downturns, inflation, and interest rate changes also pose significant threats, necessitating agile economic strategies and robust financial planning.
Operational Risk: Pertaining to the day-to-day functioning of a company, operational risk involves any event that disrupts business operations. This could range from supply chain issues, equipment failures, to human errors. Large companies must invest in effective operational risk management, including process optimization and contingency planning, to mitigate potential losses from operational setbacks.
Compliance Risk: As global regulations become more stringent and complex, compliance risk gains prominence. This involves the risk of legal or regulatory sanctions, financial loss, or damage to reputation a company might face if it fails to comply with laws, regulations, guidelines, and codes of conduct. Large corporations, often operating across multiple jurisdictions, need to stay abreast of regulatory changes and ensure strict adherence to avoid penalties and reputational damage.
Geopolitical Risk: These risks stem from political changes or instability in countries where a company operates. Geopolitical uncertainties can lead to disruptions in trade policies, currency fluctuations, and can even escalate to conflicts or sanctions. Companies must develop geopolitical risk strategies, including diversification and political risk insurance, to navigate these challenges.
Natural Disasters: Events like earthquakes, floods, and hurricanes can have devastating effects on businesses. Large companies often have extensive physical assets and global supply chains that are vulnerable to such disasters. Disaster recovery plans and insurance are vital in mitigating the impact of these unforeseen events.
Reputation Risk: In the digital age, a company's reputation can be its most valuable asset. Reputation risk involves the potential for negative publicity, misinformation, or other factors damaging a company's standing. Large corporations must actively manage their public relations, engage in corporate social responsibility, and monitor social media to safeguard their reputation.
Cybersecurity Risk: With the increasing reliance on digital technologies, cybersecurity risks have escalated. These include threats like data breaches, cyber-attacks, and ransomware. Large companies, often targets for cybercriminals, must invest in advanced cybersecurity measures and constantly update their defense mechanisms to protect sensitive data and maintain trust.
AI Risk: As artificial intelligence becomes more integrated into business operations, AI risks emerge. These include ethical considerations, biases in AI algorithms, and potential operational failures. Companies must establish AI governance frameworks and ethical guidelines to ensure responsible and effective use of AI technologies.
Legal Risk: This involves risks associated with legal constraints or lawsuits. Large companies, given their scale and scope of operations, are particularly exposed to various legal challenges, from contract disputes to intellectual property issues. Robust legal teams and proactive legal risk management are essential to navigate this complex landscape.
Logistical Risk: Involving the management of supply chains and transportation of goods, logistical risk is critical for large companies. Disruptions in supply chains, transportation delays, or failures can severely impact operations. Effective logistical planning, diversification of suppliers, and investment in logistics technology are key in mitigating these risks.
Each of these risks requires a tailored approach, considering the specific context and scope of the company. For large corporations, the integration of comprehensive risk management strategies, encompassing these diverse risk types, is not just a protective measure, but a strategic imperative for sustainable growth and competitiveness in a complex global market.
Real-world Examples of Business Risk
Geopolitical Tensions and Supply Chain Risks: The strategic importance of semiconductors in key industries like defense and aerospace, coupled with their critical applications in surveillance and artificial intelligence, has led to increased government intervention. A prime example is the ongoing trade dispute between the US and China, significantly impacting free trade and posing substantial risks to semiconductor supply chains. This geopolitical tension exemplifies how external factors can escalate into significant business risks, affecting not just individual companies but entire industries.
Global Competition in Semiconductor Manufacturing: The severe semiconductor shortage of 2021-2022 catalyzed a reassessment of reliance on Asian electronic imports by several countries. Nations like the US, Japan, and some European countries have initiated extensive support for local electronic manufacturing. While Asia Pacific, particularly with its dominance in electronic goods assembly and consumption, is unlikely to face immediate challenges, there's a looming possibility of its market share being gradually eroded. This shift highlights the risk large corporations face in maintaining supply chain stability amidst evolving global manufacturing landscapes.
Risks of Production Concentration: The concentration of semiconductor manufacturing in Asia presents a significant risk. Any major disruption in key markets such as Taiwan, China, or South Korea could instantly impact global supply chains. This risk is amplified by the tendency of semiconductor companies to source critical components from a single company or factory. Such concentration risks heighten vulnerabilities to supply disruptions, posing a threat to operational continuity and potentially leading to significant financial and reputational losses.
Industry Risk Ratings in the Electronics Sector
According to Allianz Trade's assessment of 70 countries, the electronics industry faces varied levels of risk:
Medium risk in 44 countries,
Sensitive risk in 23 countries,
High risk in 3 countries: Argentina, Russia, and Turkey.
These ratings reflect the diverse risk landscape that large corporations must navigate. The differentiation in risk levels across countries underlines the importance of a nuanced, region-specific approach to risk management, particularly for businesses operating on a global scale.
The semiconductor industry's scenario is a microcosm of the broader business risk environment. It illustrates the need for large corporations to develop sophisticated, flexible risk management strategies that can adapt to changing geopolitical climates, supply chain dynamics, and industry-specific challenges. In this complex and ever-changing world, the ability to anticipate, understand, and mitigate business risks is not just a strategic advantage but a fundamental necessity for sustained growth and resilience.
Strategies for Mitigating Business Risks in Large Organizations
Risk Management as a Key Solution
Risk management is pivotal in safeguarding organizations against the unpredictable tides of business risks. It is not merely about defensive tactics but involves a comprehensive strategy encompassing identification, assessment, and mitigation of potential threats. This approach is crucial for large organizations, where the scale of operations and the magnitude of potential risks are significantly greater.
Allianz Trade, a leader in this arena, offers specialized risk management solutions tailored to the unique needs of large corporations. Their expertise lies in understanding the nuances of various business risks and providing innovative, practical solutions. From trade credit insurance to customized risk assessment tools, Allianz Trade equips businesses with the necessary armor to protect against financial losses, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
Reducing Business Risks: Effective Approaches
For large organizations, reducing business risks requires a multifaceted strategy. Here are some effective approaches:
- Diversification: Spreading out operations, whether in terms of geographical presence, product lines, or supply chains, is a key strategy. Diversification helps mitigate risks associated with market volatility, geopolitical tensions, and industry-specific downturns.
- Technological Integration: Employing advanced technologies for risk assessment and management is vital. Tools like data analytics, AI, and machine learning can provide deep insights into risk patterns, predict potential disruptions, and optimize risk management strategies.
- Compliance and Regulatory Vigilance: Staying abreast of and complying with the latest regulatory requirements is essential. This involves regular audits, legal consultations, and adapting business practices to meet changing regulatory landscapes.
- Crisis Management Planning: Having a well-defined crisis management plan enables organizations to respond swiftly and effectively to unforeseen events, minimizing potential damages.
- Employee Training and Engagement: Employees play a crucial role in identifying and managing risks. Regular training and creating a culture of risk awareness can significantly enhance an organization's risk mitigation capabilities.
- Financial Risk Management: This includes strategies like hedging against currency fluctuations, maintaining robust cash reserves, and credit risk analysis to ensure financial stability.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Building a resilient supply chain through strategies like having multiple suppliers, investing in supply chain technology, and regular risk assessments of the supply chain can substantially reduce operational risks.
- Cybersecurity Measures: As digital risks escalate, investing in robust cybersecurity infrastructure and policies is paramount. This includes regular security audits, employee cybersecurity training, and adopting the latest in digital security technologies.
- Sustainability Practices: Incorporating sustainable and responsible business practices can mitigate risks related to environmental regulations and changing consumer preferences.
By adopting these strategies, large organizations can not only navigate the complexities of business risks but also harness them as catalysts for innovation and growth. The role of comprehensive risk management solutions like those offered by Allianz Trade becomes indispensable in this endeavor, providing the expertise and support necessary for businesses to thrive in an uncertain world.
Identifying and Managing Business Risk Factors
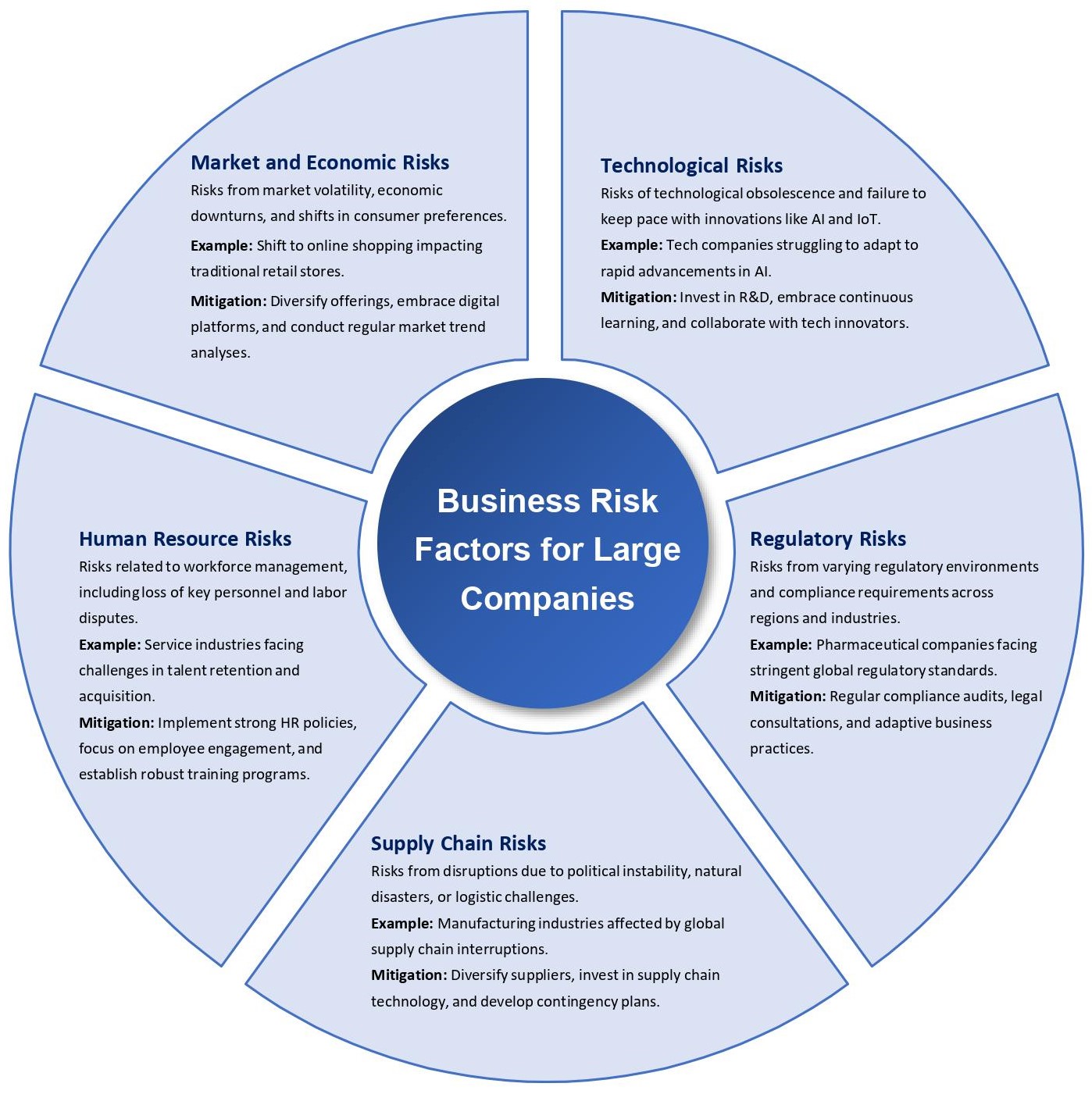
What are Business Risk Factors for Large Companies?
For large companies, business risk factors are often multi-dimensional and interlinked, varying significantly across different industries and geographies:
Market and Economic Risks: These include market volatility, economic downturns, and changes in consumer preferences. In retail, for instance, the shift to online shopping poses a significant risk to traditional brick-and-mortar stores. Geographically, companies operating in economically unstable regions face higher risks of currency fluctuations and inflation.
Technological Risks: Rapid technological advancements can render existing business models obsolete. In the tech industry, the speed of innovation is a double-edged sword, with the risk of falling behind new trends like AI and IoT.
Regulatory and Compliance Risks: These vary greatly across regions and industries. For example, the pharmaceutical industry faces stringent regulatory requirements, while financial services companies must navigate a complex web of international financial regulations.
Supply Chain Risks: Companies with global supply chains face risks from disruptions due to political instability, natural disasters, or logistic failures. These risks are particularly acute in manufacturing industries.
Human Resource Risks: This includes the risk of losing key personnel, labor disputes, or challenges in talent acquisition, which are prominent in service-oriented industries.
Protective Measures Against Emerging Risks
In addressing these varied risk factors, large companies must adopt a proactive and adaptive approach:
Cybersecurity Measures: With the rise of digital operations, cybersecurity risks like data breaches and cyber-attacks have become prominent. Protective measures include investing in robust cybersecurity infrastructure, continuous monitoring, and employee training in cyber hygiene.
AI and Technological Risk Management: As companies integrate AI into their operations, managing the risks associated with AI decisions becomes crucial. This involves setting up ethical guidelines for AI use, ensuring transparency in AI processes, and continuously monitoring AI systems for unexpected behaviors.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation: The business environment is in constant flux, necessitating ongoing monitoring of risk factors. This includes keeping abreast of market trends, regulatory changes, and technological advancements, and adjusting business strategies accordingly.
Diversification: Diversifying markets, products, and supply chains can spread risk and reduce dependence on a single source, which is crucial for mitigating risks associated with specific industries or geographies.
Crisis Management and Business Continuity Planning: Developing comprehensive crisis management and business continuity plans ensures that companies are prepared to respond effectively to disruptions, minimizing impact on operations.
Stakeholder Engagement and Communication: Regular communication with stakeholders, including employees, customers, and suppliers, helps in early identification of risks and collaborative development of mitigation strategies.
By thoroughly understanding and actively managing these risk factors, large companies can not only safeguard their present operations but also strategically position themselves for future growth and success in an increasingly unpredictable business landscape.
Summarizing the Importance of Managing Business Risks
Throughout this article, we've explored the multifaceted nature of business risks that large corporations face. From the dynamic economic and market risks, operational complexities, and regulatory challenges to the evolving threats posed by cybersecurity and AI, the scope is vast and varied. We've seen how these risks differ across industries and geographies, necessitating a tailored approach in each case.
Effective risk management is about understanding these nuances, anticipating potential challenges, and being prepared with adaptive strategies. It involves a holistic view of the business environment, leveraging technology for risk assessment, ensuring compliance, and fostering a culture of risk awareness within the organization.
Explore Allianz Trade’s Trade Finance Products
In this context, partnering with Allianz Trade, a leader in trade credit insurance and risk management solutions, becomes a strategic decision. Allianz Trade's expertise in offering tailored risk management solutions is an invaluable asset for large companies looking to safeguard their operations and capitalize on market opportunities.
Allianz Trade's trade finance products are designed to address the unique challenges faced by large corporations. They provide not just protection against a range of business risks but also the support to navigate through them effectively. By partnering with Allianz Trade, companies gain access to a wealth of experience, comprehensive risk assessments, and innovative solutions that are crucial in today’s fast-paced and uncertain business environment.
Highlighting the Benefits of Partnering with Allianz Trade for Large Companies
The benefits of this partnership are multifaceted:
● Tailored Solutions: Customized risk management solutions that cater to the specific needs of your business.
● Global Expertise: Access to global insights and trends, helping companies stay ahead in a competitive market.
● Risk Mitigation: Enhanced capabilities to identify, assess, and mitigate diverse business risks.
● Operational Stability: Ensuring business continuity even in the face of disruptions.
● Competitive Advantage: Leveraging risk management for strategic advantage and sustainable growth.
In conclusion, understanding and managing business risks is an essential part of steering a large company towards success. With Allianz Trade's expertise and comprehensive solutions, companies can confidently face these challenges, turning risks into opportunities for advancement. We encourage businesses to explore Allianz Trade’s trade finance products and experience the difference that a dedicated and specialized partner can make in navigating the complex world of business risks.



